Introduction
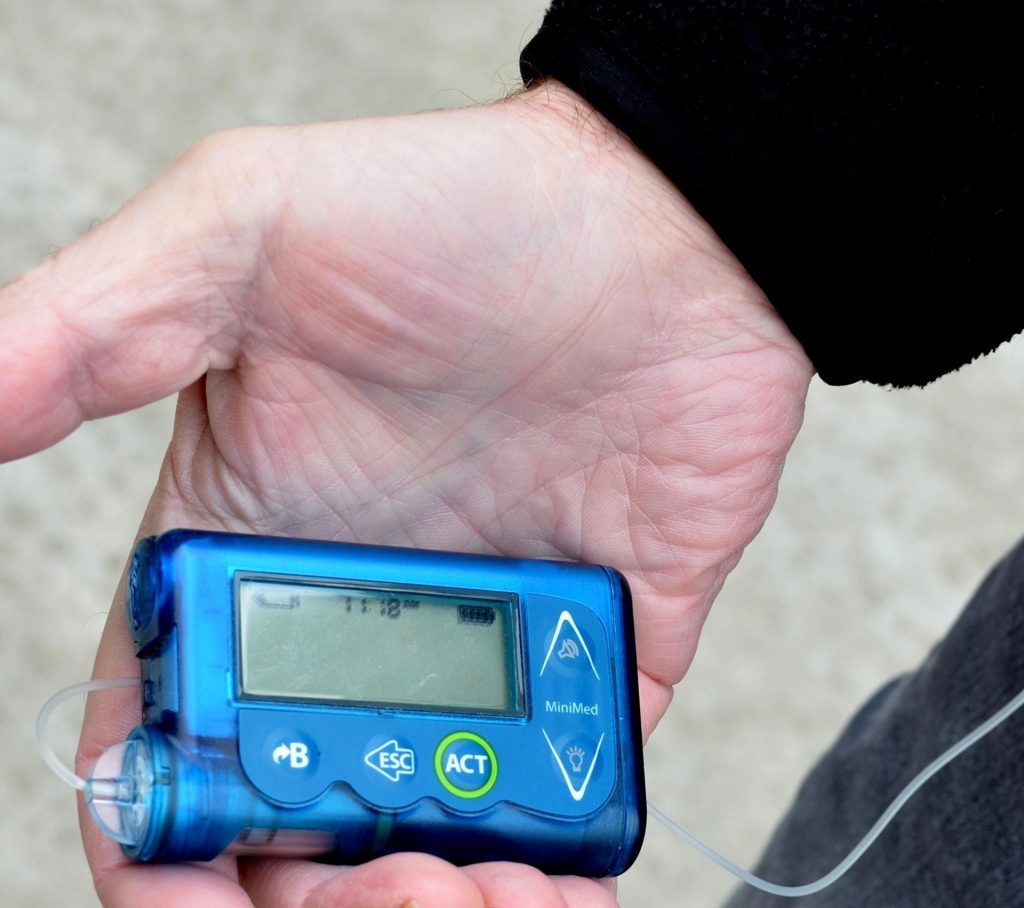
Insulin pumps are medical devices that have revolutionized the management of diabetes. These devices are small, wearable, computerized devices that deliver insulin to the body continuously or in programmed doses, mimicking the function of a healthy pancreas. Insulin pumps have become increasingly popular among people with diabetes due to their ability to offer improved blood sugar control, increased flexibility, and better quality of life. In this article, we will discuss what insulin pumps are, how they work, and their benefits and drawbacks.
What are Insulin Pumps?
Insulin pumps are small electronic devices that deliver insulin to the body through a thin, flexible tube called a cannula. The cannula is inserted under the skin, typically on the abdomen, and remains in place for several days before it needs to be replaced. The pump is programmed to deliver insulin at specific times and rates, based on the individual’s needs. The pump holds a reservoir of insulin, which can be refilled as needed.
How do Insulin Pumps Work?
Insulin pumps work by delivering insulin in two different ways: basal and bolus insulin delivery. Basal insulin is delivered continuously, mimicking the background insulin production of a healthy pancreas. This helps to maintain a stable blood sugar level throughout the day and night. Bolus insulin, on the other hand, is delivered as a quick burst of insulin to cover meals or correct high blood sugar levels. This allows for more flexibility in meal planning and offers better control over blood sugar levels.
Insulin pumps are programmed to deliver different rates of insulin at different times of the day, depending on the individual’s needs. The pump can be adjusted to deliver more or less insulin depending on factors such as physical activity, illness, and stress. This level of flexibility is not possible with traditional insulin injections.
Benefits of Insulin Pumps
Insulin pumps offer several benefits over traditional insulin injections. Here are some of the main advantages:
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: Insulin pumps allow for better blood sugar control, which can reduce the risk of long-term complications of diabetes such as blindness, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
- More Flexibility: Insulin pumps offer greater flexibility in terms of meal planning and timing of insulin delivery. This can help people with diabetes to maintain a more normal lifestyle.
- Reduced Risk of Hypoglycemia: Insulin pumps can reduce the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) by delivering insulin more precisely and in smaller amounts.
- Improved Quality of Life: Insulin pumps can improve the quality of life for people with diabetes by reducing the need for frequent injections and offering greater freedom and flexibility.
Drawbacks of Insulin Pumps
Despite the benefits of insulin pumps, there are also some drawbacks to consider. Here are some of the main disadvantages:
- Cost: Insulin pumps can be expensive, and not all insurance plans cover them.
- Learning Curve: There is a learning curve associated with using an insulin pump, and it can take time to become comfortable with the device and the programming.
- Maintenance: Insulin pumps require regular maintenance, including replacing the cannula and reservoir, and monitoring blood sugar levels closely.
- Inconvenience: Insulin pumps can be bulky and require frequent monitoring and adjustments. This can be inconvenient for some people.
Conclusion
Insulin pumps are a valuable tool for people with diabetes who are looking for better blood sugar control, greater flexibility, and improved quality of life. While there are some drawbacks to consider, the benefits of insulin pumps outweigh the disadvantages for many people. If you are considering an insulin pump, talk to your healthcare provider to see if it is a good option for you. With proper training and support, an insulin pump can be a valuable tool in managing your diabetes.